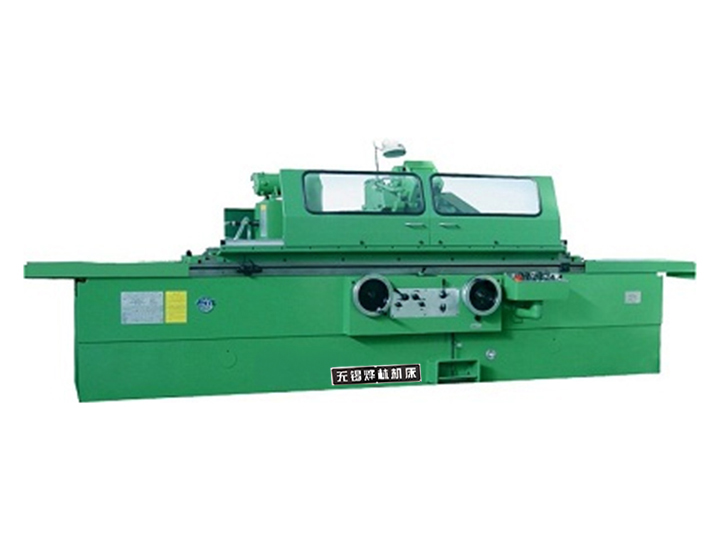
As a core equipment in the mechanical manufacturing field, grinding machines achieve precision grinding of workpiece surfaces. Their operation must strictly follow specifications to balance precision and safety. The following instructions cover five aspects: operational preparation, parameter setting, process control, problem handling, and safety regulations.
I. Pre-operation Preparation
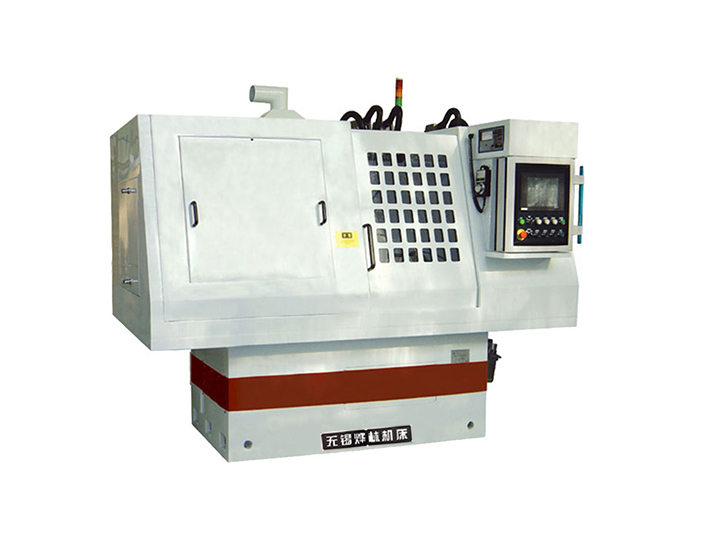

Before operation, thoroughly inspect the equipment status. Focus on confirming that the grinding wheel is free of cracks and securely installed, the coolant reserve is sufficient with unobstructed pipelines, the lubrication system operates normally, and electrical safety meets standards. Operators must wear protective glasses and avoid wearing gloves or jewelry that could be entangled to ensure personal safety.
II. Workpiece Clamping and Parameter Setting
Workpieces must be firmly fixed using fixtures such as bench vices or electromagnetic chucks to ensure accurate positioning and moderate clamping force. Select the grinding wheel type, rotational speed, feed rate, and grinding depth based on workpiece material hardness, heat treatment condition, and processing requirements (e.g., rough grinding or precision grinding). Rough grinding can use a larger feed rate to improve efficiency, while precision grinding requires a smaller feed rate to ensure surface accuracy.
III. Grinding Process Control
After starting, idle the grinding wheel for 1-2 minutes and confirm no abnormalities before grinding. Continuously monitor coolant flow and temperature during the process to ensure effective cooling and chip flushing. Simultaneously listen to the grinding sound and observe the spark pattern; immediately stop the machine if abnormal vibration or noise is detected. Regularly dress the grinding wheel (e.g., using a diamond pen) to restore its cutting performance and geometric shape.
IV. Common Problem Handling
If vibration marks appear on the machined surface, check the grinding wheel balance, workpiece clamping stability, or machine tool foundation status. If surface roughness does not meet standards, optimize grinding wheel selection, adjust parameters, or increase coolant flow. Surface burns on workpieces are mostly caused by excessive grinding volume, overly hard grinding wheels, or insufficient cooling; reduce feed rate, replace with a softer grinding wheel, or enhance cooling.
V. Safety Regulations
During operation, strictly prohibit contact with rotating components; measurement or adjustment must be performed with the machine stopped. After operation, promptly clean chips and coolant, reset the operating handle. Regularly lubricate moving parts to extend equipment lifespan.
The efficient and safe use of grinding machines relies on standardized operation, meticulous parameter adjustment, and strict maintenance. For high-precision demand scenarios (such as aerospace and auto parts processing), it is recommended to select equipment with stable performance.